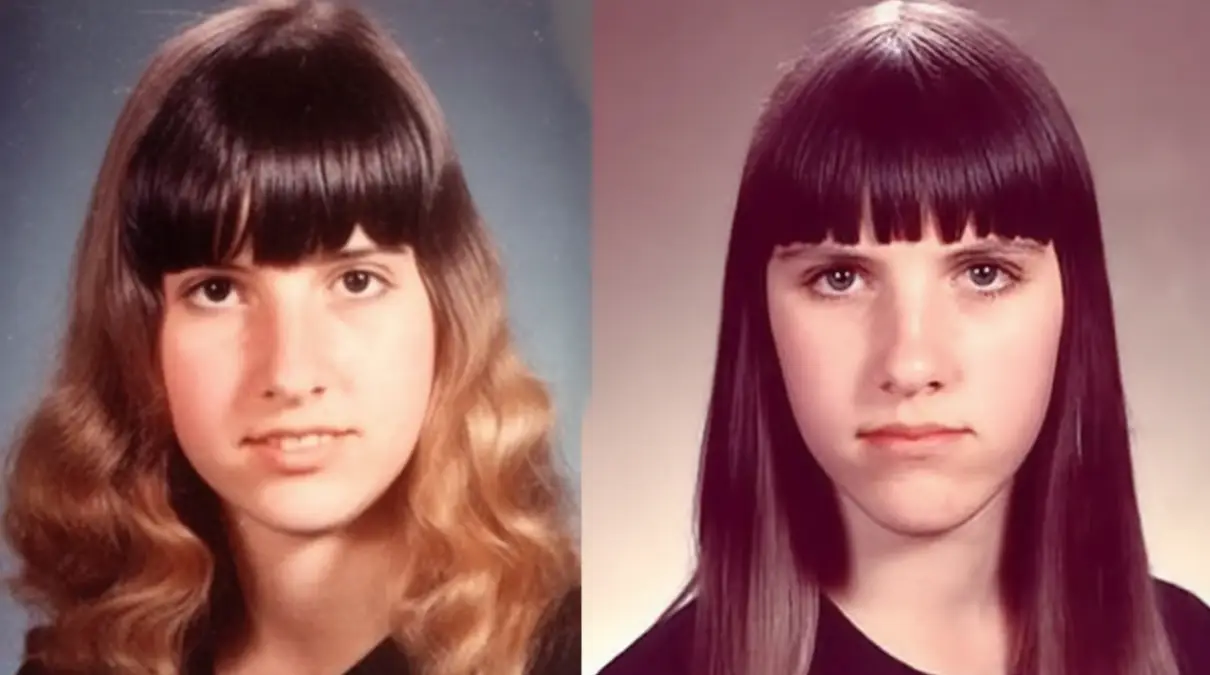Tag: Michigan
-
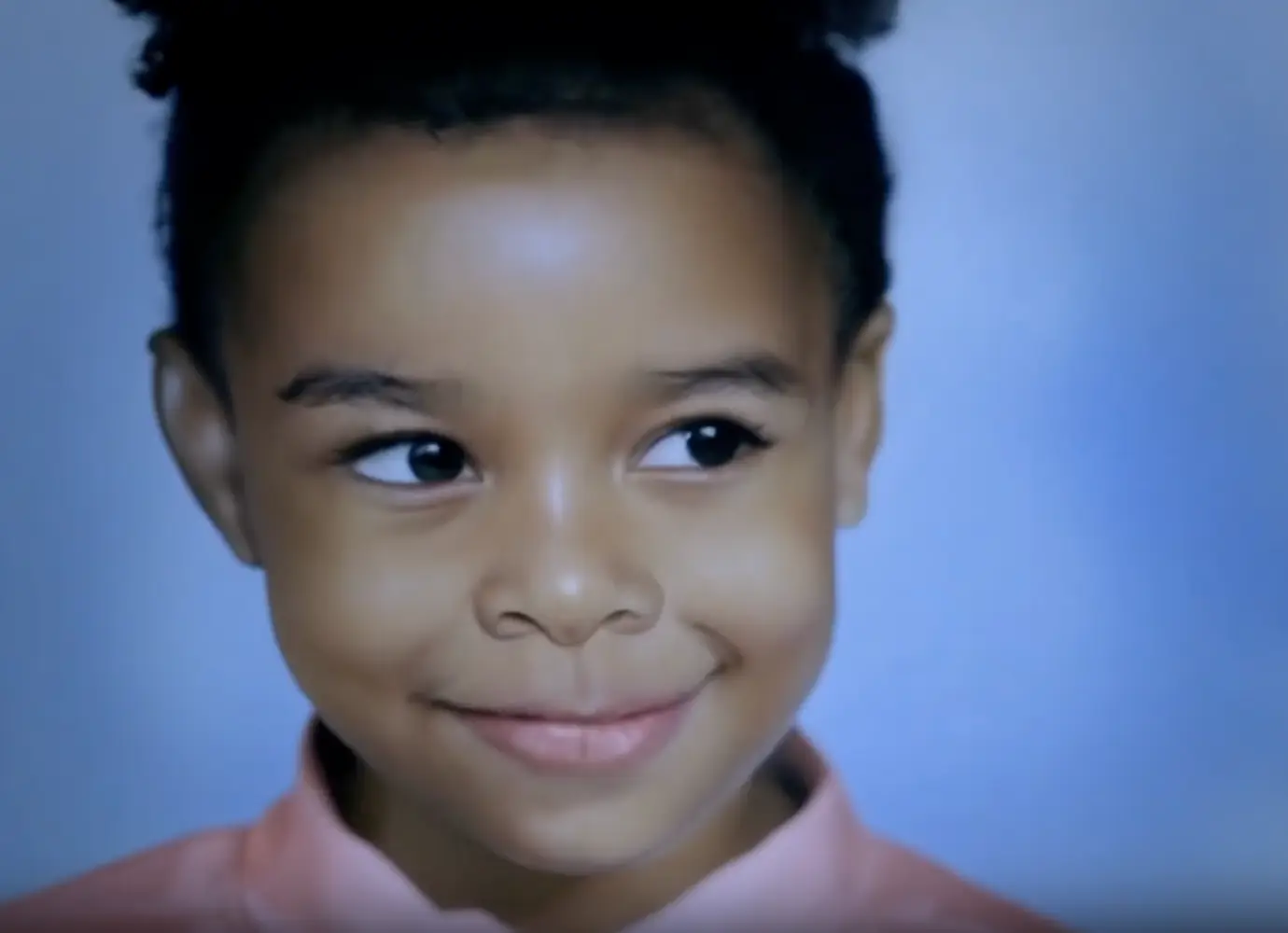
Where Is Caidee Christine Yarbro?
Vanished Without a Trace Missing person in Michigan. A Michigan community is holding its breath. Fourteen-year-old Caidee Christine Yarbro vanished after leaving school on Friday, May 9, 2025. She didn’t go home, nor did she check in with anyone. With each passing hour, the sense of urgency continues to grow. Caidee Christine Yarbro: A Normal […]
-
Missing Endangered Person in Michigan: Devlin Tait
Urgent Call to Help Locate Devlin Tait Missing person in Michigan. Lake Odessa, Michigan — The Ionia County Sheriff’s Office is actively searching for 18-year-old Devlin Tait, a vulnerable young man with special needs. He was last seen on April 21, 2025, around 8:21 p.m., at Carl’s Supermarket in Lake Odessa. Since his disappearance, concern […]
-
Reasons for Losing Keys in Michigan
lost keys.Losing Keys in Michigan. Michigan is a state of lakes, forests, and busy cities. People lose keys everywhere—on frozen sidewalks, in deep snow, and at crowded stadiums. The state’s unique weather and lifestyle contribute to this problem. Losing Keys in Michigan 1. Dropped in the Snow and Ice Michigan winters are brutal. Snow piles […]
-
Find Lost Pets with the Nfound App
Find Lost Pets. Losing a pet is a devastating experience. Every year, millions of pets go missing, and the search for them often feels overwhelming. Whether it’s a dog that ran away or a cat that wandered off, pet owners desperately search for ways to bring their furry friends home. The Nfound app provides a […]
-
Search for Missing Cats and Dogs in Michigan
Pets Go Missing. Missing Cats and Dogs in Michigan. The state’s forests, lakes, and cities create many places where pets can disappear. Acting fast and using the right tools improves recovery chances. Missing Cats and Dogs in Michigan. Why Pets Go Missing in Michigan Michigan’s diverse landscape creates risks for missing pets. In rural areas, […]
-
Missing Pets in the USA: Finding Them with Nfound App
Missing Pets in the USA. Each year, thousands of pets go missing across the United States. Pet owners experience immense stress and worry when their beloved animals disappear. Whether it’s a lost dog, cat, or exotic pet, finding a missing animal quickly is crucial. The Nfound app offers a modern solution to this age-old problem. […]
-
|by NFound | Company news, for parents, for sexual slavery victims, for teenagers, Lost and Found, parents and loved ones support, Psychology Blog, Support, the child psychologist
Leave a Missing Person Notice in Michigan: A Critical Step in Reuniting Families
Leave a Missing Person Notice in Michigan. When someone goes missing in Michigan, time is critical. Prompt action can make a significant difference in locating a missing person. One effective way to start the search is by leaving a missing person notice. With technological advances, it’s easier than ever to reach a wide audience quickly. […]
-
|by NFound | Company news, for parents, for sexual slavery victims, for teenagers, parents and loved ones support, Psychology Blog, Real Story, the child psychologist
The Bianca Jones Case: The Mystery of a Missing Two-Year-Old
Missing person in Detroit . In December 2011, a tragedy struck Detroit. Two-year-old Bianca Jones disappeared, leaving behind many unanswered questions and a grieving family. The case shocked the public, and the search became one of the most discussed in the United States. Bianca Jones: The Day Bianca Disappeared On December 2, 2011, her father, […]
-
|by NFound | for parents, for sexual slavery victims, for teenagers, Lost and Found, parents and loved ones support, Psychology Blog, Real Story, the child psychologist
The Mystery of Patricia Spencer and Pamela Hobley’s Disappearance
A Halloween Night That Turned Into a Nightmare. Missing persons. Patricia Spencer and Pamela Hobley’s Disappearance. On October 31, 1969, in Oscoda, Michigan, two teenage girls disappeared. Sixteen-year-old Patricia Spencer and fifteen-year-old Pamela Hobley were heading to a Halloween party. The evening was supposed to be filled with fun but turned into the start of […]
Michigan (M), located in the Great Lakes region of the upper Midwestern United States, is known for its diverse culture, rich history, and stunning natural beauty. It is the only state to consist of two peninsulas, the Lower Peninsula and the Upper Peninsula, separated by the Straits of Mackinac. M is surrounded by four of the five Great Lakes: Lake Superior, Lake Michigan, Lake Huron, and Lake Erie.
Michigan: Historical Overview
The Great Lakes State’s history is rich and varied. It is deeply connected to the indigenous peoples. The Ojibwe, Odawa, and Potawatomi tribes originally inhabited the region. European exploration began in the 17th century. French explorers like Étienne Brûlé mapped the area. Father Jacques Marquette was also among the first explorers. Michigan became a fur trade hub. French and later British settlers were attracted to it.
In 1837, the state joined the Union as the 26th state. The early economy was driven by lumber, mining, and agriculture. Rich copper and iron deposits were discovered in the Upper Peninsula. This discovery further boosted economic growth.
Economic Development
The Great Lakes State is famously known as the birthplace of the American automotive industry. In the early 20th century, industrialists like Henry Ford revolutionized automobile manufacturing with the introduction of assembly line production techniques. Detroit, the state’s largest city, became synonymous with the automotive industry, earning the nickname “Motor City.” Major automakers such as General Motors, Ford, and Chrysler established their headquarters in Detroit, shaping the city’s identity and economy.
Today, The Great Lakes State economy is diverse and includes manufacturing, agriculture, tourism, and technology. The state is a leading producer of cherries, apples, and blueberries, and its agricultural sector is bolstered by a wide variety of crops and livestock.
Natural Beauty and Tourism
The Great Lakes State natural beauty is one of its most defining features. The state boasts over 3,200 miles of freshwater coastline, more than any other state in the U.S. except Alaska. This extensive coastline offers countless opportunities for recreational activities such as boating, fishing, and swimming. The Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore, Pictured Rocks National Lakeshore, and Isle Royale National Park are just a few of the state’s renowned natural attractions.
The Upper Peninsula, often referred to as “The U.P.,” is known for its rugged terrain. It has dense forests and stunning waterfalls. It is a popular destination for outdoor enthusiasts. People who enjoy hiking, camping, and snowmobiling visit it often.
The Lower Peninsula is shaped like a mitten. It offers a mix of urban and rural landscapes. There are vibrant cities such as Grand Rapids, Ann Arbor, and Lansing. These cities complement the picturesque countryside.
Cultural and Educational Institutions
М is home to several prestigious universities and colleges, including the University of М in Ann Arbor, The Great Lakes State State University in East Lansing, and Wayne State University in Detroit. These institutions contribute to the state’s reputation for academic excellence and research innovation.
Culturally, The Great Lakes State has a rich musical heritage, particularly in Detroit, which played a pivotal role in the development of Motown music in the 1960s. The city produced legendary artists such as Diana Ross, Stevie Wonder, and Marvin Gaye. Additionally, М has a vibrant arts scene, with numerous theaters, museums, and galleries showcasing the state’s creative talent.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Like many states, М faces challenges, including economic disparities, environmental concerns, and urban revitalization efforts. The decline of the automotive industry in recent decades has necessitated economic diversification and the pursuit of new industries, such as technology and renewable energy.
Efforts to address environmental issues, particularly those related to water quality and conservation, are ongoing. The state has made significant strides in protecting its natural resources and promoting sustainable practices.
Conclusion
Michigan’s unique combination of natural beauty, industrial heritage, and cultural richness make it a fascinating and dynamic state. As it continues to evolve and adapt to changing economic and environmental landscapes, Michigan remains a vital part of the American story, offering a blend of history, innovation, and natural splendor.